NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles Ex 12.1
Ex 12.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
The radii of the two circles are 19 cm and 9 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle which has a circumference equal to the sum of the circumferences of the two circles.
Solution:

Ex 12.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
The radii of two circles are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find the radius of the circle having area equal to the sum of the areas of the two circles.
Solution:

Ex 12.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
The given figure depicts an archery target marked with its five scoring regions from the center outwards as Gold, Red, Blue, Black, and White.
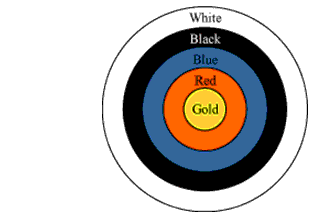
The diameter of the region representing Gold score is 21 cm and each of the other bands is 10.5 cm wide. Find the area of each of the five scoring regions.
Solution:


Formulae Handbook for Class 10 Maths and Science
Ex 12.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
The wheels of a car are of diameter 80 cm each. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is travelling at a speed of 66 km per hour?
Solution:

Ex 12.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
Tick the correct answer in the following and justify your choice: If the perimeter and the area of a circle are numerically equal, then the radius of the circle is
(a) 2 units
(b) n units
(c) 4 units
(d) 7 units
Solution:

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles (Hindi Medium) Ex 12.1







Class 10 Maths Areas Related To Circles Mind Maps
Terms Related To Circle
(i) Chord: A line segment joining any two points on a circle.
(ii) Arc: A piece of a circle between two points on the circle is called an arc.
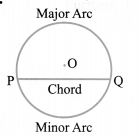
The arc less than the semicircular arc is called minor arc and the one greater than the semi-circular arc is called major arc.
(iii) Sector: The portion of a circular region enclosed by two radii and the corresponding arc is called a sector of the circle.
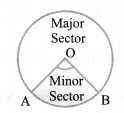
Sector smaller than the semi-circle is called minor sector and the sector larger than the semi-circle is called major sector.
(iv) Segment: The portion of a circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc is called a segment of the circle.
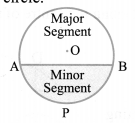
The segment bounded by the chord and the minor arc intercepted by the chord is called minor segment and the segment bounded by the chord and the major arc intercepted by the chord is called major segment.
Circle
The set of all points in a plane which are at a fixed distance from a fixed point in the plane is called circle. The fixed point is called centre and the fixed distance is called radius of the circle
Circumference and Area of a Circle
(i) The circumference of a circle is defined as distance covered by travelling once around a circle and is given by C = 2πr = πd
where r = radius of the circle and d = diameter of the circle.
(ii) The Area of a circle of radius r is given by,
A = (pi r^{2}=frac{pi}{4} d^{2}) where, d = diameter of the circle.
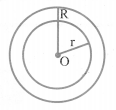
(iii) Area of a circular ring:
The area of the circular path or ring is given by the difference of the area of outer circle and the area of inner circle.
Area of circular ring = n(R2 – r2)
Length of an Arc and Area of Sector
(i) The length of an arc of a sector of an angle 9 is given by,
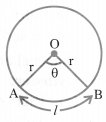
(ii) The area of the sector AOB of angle 0 is given by,
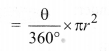
This is the area of minor sector.
∴ area of major sector AOB
= πr2 – Area of a minor sector AOB
Area of Segment
(i) Area of segment APB = Area (sector OAPB) – Area(∆OAB)
This is the area of minor segment.
∴ area of major segment AQB = πr2 – Area of minor segment APB
(ii) If θ is the central angle, then the area of segment APB
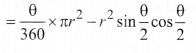
Comments are closed